On the improvement of PEC activity of hematite thin films deposited by high-power pulsed magnetron sputtering method
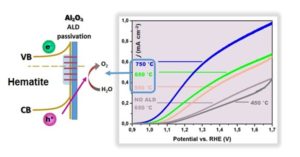 We have effectively combined the high impulse magnetron sputtering (HiPIMS) synthetic approach with another powerful deposition method of atomic layer deposition (ALD) to fabricate highly active photoanodes based on very thin hematite films (~ 50 nm) deposited by HiPIMS and alumina (Al2O3) ultra-thin films coated over the hematite by ALD. In this way the backward recombination of photogenerated electrons and holes was highly reduced due to the passivation of undesirable surface states acting as traps. Moreover the overpotential needed to initiate the PEC oxidation reaction was significantly reduced, which was shown as a considerable shift of the photocurrent onset potential to the more cathodic region. It was also demonstrated for the first time that the one annealing step of the as-deposited Fe2O3/as-deposited Al2O3 is more effective due to relaxation of the hematite film stress reducing the generation of the surface defects than two separate consecutive annealing steps. The maximal shift of the photocurrent onset potential by 0.1 V vs. RHE was achieved for system of HiPIMS hematite/ALD (2 nm) alumina passivation layer annealed simultaneously at 650◦C for 40 min. On the other hand, the highest photocurrent value reached at 1.23 V vs. RHE was 0.48 mA/cm2 of the identical system but annealed together at 750◦C for 40 min. This work has been done in cooperation with Iniversity in Nebraska – Lincoln, NE, USA.
We have effectively combined the high impulse magnetron sputtering (HiPIMS) synthetic approach with another powerful deposition method of atomic layer deposition (ALD) to fabricate highly active photoanodes based on very thin hematite films (~ 50 nm) deposited by HiPIMS and alumina (Al2O3) ultra-thin films coated over the hematite by ALD. In this way the backward recombination of photogenerated electrons and holes was highly reduced due to the passivation of undesirable surface states acting as traps. Moreover the overpotential needed to initiate the PEC oxidation reaction was significantly reduced, which was shown as a considerable shift of the photocurrent onset potential to the more cathodic region. It was also demonstrated for the first time that the one annealing step of the as-deposited Fe2O3/as-deposited Al2O3 is more effective due to relaxation of the hematite film stress reducing the generation of the surface defects than two separate consecutive annealing steps. The maximal shift of the photocurrent onset potential by 0.1 V vs. RHE was achieved for system of HiPIMS hematite/ALD (2 nm) alumina passivation layer annealed simultaneously at 650◦C for 40 min. On the other hand, the highest photocurrent value reached at 1.23 V vs. RHE was 0.48 mA/cm2 of the identical system but annealed together at 750◦C for 40 min. This work has been done in cooperation with Iniversity in Nebraska – Lincoln, NE, USA.
Kment, S.; Schmuki, P.; Schubert, E.; Zboril, R. et al. On the improvement of PEC activity of hematite thin films deposited by high-power pulsed magnetron sputtering method, Appl. Catal. B-Environ., 2015, 165, 344-350.


