Publication in PLOS ONE
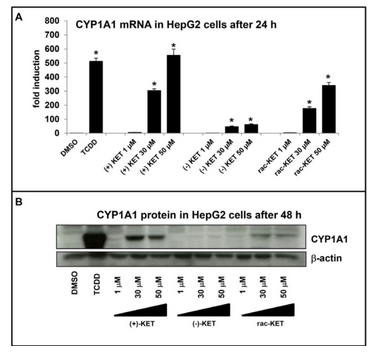 The publication “Enantiospecific Effects of Ketoconazole on Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor“ was recently published in the respected journal Plos ONE (PLoS One. 2014 Jul 7;9(7):e101832, IF2012 = 3,73). The work studies enantiospecific effects of antifungal drug ketoconazole (KET) that is clinically used as a racemic mixture of two cis-enantiomers (2R,4S)-(+)-KET a (2S,4R)-(2)-KET on aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) signaling pathway. The results revealed that both enantiomers are weak ligands for AhR but (+)-KET has stronger effect on induction of AhR target genes compared to (-)-KET both in human hepatoma cells HepG2 and in primary human hepatocytes.
The publication “Enantiospecific Effects of Ketoconazole on Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor“ was recently published in the respected journal Plos ONE (PLoS One. 2014 Jul 7;9(7):e101832, IF2012 = 3,73). The work studies enantiospecific effects of antifungal drug ketoconazole (KET) that is clinically used as a racemic mixture of two cis-enantiomers (2R,4S)-(+)-KET a (2S,4R)-(2)-KET on aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) signaling pathway. The results revealed that both enantiomers are weak ligands for AhR but (+)-KET has stronger effect on induction of AhR target genes compared to (-)-KET both in human hepatoma cells HepG2 and in primary human hepatocytes.
31/7/2014


